| 1617 | Sweden occupies the banks of the River Neva, setting up the Nyenschantz Fortress and cutting Russia off from the Baltic. |
| 1700 | Beginning of the Great Northern War between Russia and Sweden. Russia aims to regain its access to the Baltic. |
| 1702 | The Swedish Noteborg Fortress on the River Neva is captured. This will be the basis for the future St Petersburg. |
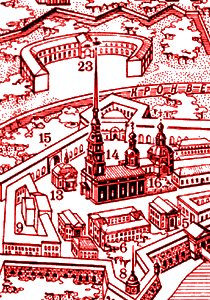
| 1703 | Nyenschantz Fortress falls to the Russians. Foundation stone lain by Peter I (the Great) for the Peter and Paul Fortress on Zayachi Ostrov (Hare Island) downstream from Nyenschantz. City of St Petersburg founded at same time. Conceived as an architecturally splendid centre of culture and learning. Built by Swedish prisoners of war, Finns and Russian serfs. |
| 1704 | Foundation stone for Admiralty building lain. |
| 1712 | Decree issued ordering people to move to St Petersburg from across Russia. Other decrees include the banning of any building in stone elsewhere in Russia to overcome a shortage of masons, and every citizen owning more than 500 serfs being ordered to build a two-storey stone building in the new city. |
| 1715 | Military academy opens. |
| 1719 | First St Petersburg museum opens. |
| 1721 | Russia wins Great Northern War. |
| 1724 | Peter I moves state institutions to St Petersburg and it becomes official capital of Russia. |
| 1725 | Science academy opens. Peter I dies. Heirs spend lavishly on the city, summoning the best Russian and foreign architects. |
| 1741 | Beginning of the reign of Elisabeth Petrovna. During her reign construction starts on Winter Palace (architect Bartolomo Rastrelli), Smolny Cathedral and Catherine Palace. |
| 1762 | Catherine II (the Great)’s reign begins having desposed of her husband, Peter III. Move from baroque to Classical style architecture in new building projects. Construction of Marble Palace (Rinaldi), Pavlovsk Palace (Cameron) and Academy of Fine Arts (Vallin de la Mothe) during her reign. Neva Islands remodelled with wide avenues, parks and series of palaces. Winter Palace completed. Small Hermitage built and Old Hermitage begun. Catherine dies 1796. Subsequent tsars commission further grand buildings but lack unity and accomplishment of early designs. |
| 1812 | Large memorials erected to mark victory over Napoleon. |
| 1824 | City seriously damaged in floods (city built upon 44 islands and a marshy plain so flooding was a regular hazard). |
| 1825 | Decembrist
Uprising. Failed attempt to force |
| 1835 | First
Russian railway links St Petersburg to |
| 1851 | Regular train services to and from Moscow. |
| 1879 | Founding of the revolutionary Narodnaya Volya (People’s Will) group in St Petersburg. |
| 1881 | Narodnaya Volya organises assassination of Alexander II. |
| 1890 | Lenin
visits St Petersburg for first time to |
| 1893 | Lenin and his party begin political education of the St Petersburg factory workers. |
| 1895 | Lenin
sets up Union for the Struggle for the |
| 1905 | 140,000 workers march on the Winter Palace calling for reforms. 100 killed. Some concessions made after sections of army and navy join revolt. Duma (Russian Parliament) established. |
| 1914 | Beginning of World War One. St Petersburg’s name changed to the more Russian sounding Petrograd. |
| 1917 | Nicholas II abdicates following the February Revolution. Kerensky heads provisional government. Lenin returns from exile in Switzerland to St Petersburg but fails to set off a proletarian revolution. Goes into hiding in July. 10 October – Bolshevik Central Committee decides on an armed revolt. 26 October – Committee gains control of the city. |
| 1918 | Bolshevik government moves to Moscow. |
| 1924 | Death of Lenin. Petrograd renamed Leningrad in his honour. |
| 1941-44 | Siege of Leningrad. |
| 1950 | Kirov Stadium built. |
| 1955 | First metro opened. |
| 1965 | Leningrad named City of Valour. |
| 1991 | Attempted coup against Mikhail Gorbachev hastens end of USSR. Leningrad renamed St Petersburg after referendum. |
| 1998 | Remains of Nicholas II and his family buried in the Cathedral of St Petersburg’s Peter and Paul Fortress. |